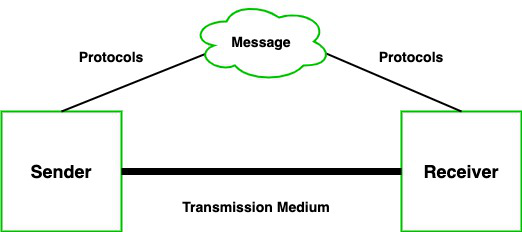
Communication channels are the medium that connects two or more workstations. Workstations can be connected by either wired media or wireless media. It is also known as a transmission medium. The transmission medium or channel is a link that carries messages between two or more devices. We can group the communication media into two categories:
- Guided media transmission
- Unguided media transmission
1. Guided Media: In this transmission medium, the physical link is created using wires or cables between two or more computers or devices, and then the data is transmitted using these cables in terms of signals. Guided media transmission of the following types:
1. Twisted pair cable: It is the most common form of wire used in communication. In a twisted-pair cable, two identical wires are wrapped together in a double helix. The twisting of the wire reduces the crosstalk. It is known as the leaking of a signal from one wire to another due to which signal can corrupt and can cause network errors. The twisting protects the wire from internal crosstalk as well as external forms of signal interference. Types of Twisted Pair Cable :
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP): It is used in computers and telephones widely. As the name suggests, there is no external shielding so it does not protects from external interference. It is cheaper than STP.
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP): It offers greater protection from crosstalk due to shield. Due to shielding, it protects from external interference. It is heavier and costlier as compare to UTP.
2. Coaxial Cable: It consists of a solid wire core that is surrounded by one or more foil or wire shields. The inner core of the coaxial cable carries the signal and the outer shield provides the ground. It is widely used for television signals and also used by large corporations in building security systems. Data transmission of this cable is better but expensive as compared to twisted pair.
3. Optical fibers: Optical fiber is an important technology. It transmits large amounts of data at very high speeds due to which it is widely used in internet cables. It carries data as a light that travels inside a thin glass fiber. The fiber optic cable is made up of three pieces:
- Core: Core is the piece through which light travels. It is generally created using glass or plastic.
- Cladding: It is the covering of the core and reflects the light back to the core.
- Sheath: It is the protective covering that protects fiber cable from the environment.
2. Unguided Media: The unguided transmission media is a transmission mode in which the signals are propagated from one device to another device wirelessly. Signals can wave through the air, water, or vacuum. It is generally used to transmit signals in all directions. Unguided Media is further divided into various parts :
1. Microwave: Microwave offers communication without the use of cables. Microwave signals are just like radio and television signals. It is used in long-distance communication. Microwave transmission consists of a transmitter, receiver, and atmosphere. In microwave communication, there are parabolic antennas that are mounted on the towers to send a beam to another antenna. The higher the tower, the greater the range.
2. Radio wave: When communication is carried out by radio frequencies, then it is termed radio waves transmission. It offers mobility. It is consists of the transmitter and the receiver. Both use antennas to radiate and capture the radio signal.
3. Infrared: It is short-distance communication and can pass through any object. It is generally used in TV remotes, wireless mouse, etc.