Virtual networks can be thought of as separate networks within a larger network. Administrators can create a separate network segment consisting of a range of subnets (or a single subnet) and control traffic that flows through the cloud network. Depending on your business needs, you can implement your network using cloud technology from a cloud service provider (CSP).
The key difference for cloud administrators and architects when it comes to designing cloud networking solutions is the amount of control needed to have over the hardware. When you implement cloud networking with a CSP, you have little control over — and likely little knowledge about — the design of the CSP’s network. Because of this limitation, virtual networks are often the go-to choice when you want to provide secure network isolation.
With a cloud solution, these virtual networks are known as VNets or Virtual Private Clouds (VPC). These act as a representation of a network in the cloud, giving you a cloud network.
Virtual networks provide the following benefits:
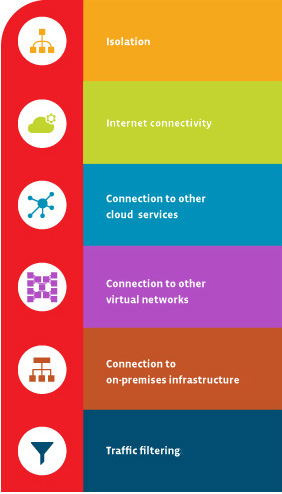
- Isolation
You can keep networks isolated from one another to ensure security and for purposes of development, quality assurance and deployment of cloud networks. - Internet Connectivity
Each virtual network can be configured to access or deny access to the internet, or to limit access to specific destinations on the internet if needed. - Connection to Other Cloud Services
Virtual networks often need a connection to CSP services. This allows the network to utilize services offered by the CSP. Providers typically allow for configuration of routing tables, domain name resolution, firewall and related items to manage the connections to your virtual networks. - Connection to Other Virtual Networks
This allows you to interconnect your virtual networks when necessary while maintaining control over connections. - Connection to On-Premises Infrastructure
Part of the flexibility of a virtual network is the ability to control connections. You can connect your virtual network to on-premises systems. Often this type of configuration is for end users to access a secure private cloud network or done as part of a hybrid cloud implementation. - Traffic Filtering
Most secure connections involve filtering. Normally, this involves filtering items by source IP address and port, destination IP address and port, and particular protocol. This gives cloud computing engineers increased control over the communications occurring on your network.